Since the Central Bank of Nigeria implemented a cashless policy in 2012, electronic payments have increased in Nigeria.
In 2012, for example, there were 4.4 million NIP transactions valued $3.9 trillion ($8.5 billion). Eleven years later, the frequency of NIP transactions has increased more than 1,150 times, while the value of those transactions has increased about 100 times. That is completely ridiculous. It’s no surprise that Nigeria will process more real-time payments volume than the United States in 2021.
Many new firms have formed, as expected, to ride the real-time payment wave and deliver more payments online. In the seven years between 2014 and 2021, for example, the number of fully CBN-licensed PTSPs doubled.
Today, however, is not the day for PTSPs. It is instead intended for PSSPs, or those who develop software for online payment collection. A Payment Gateway is a common example of the software PSSPs develop for payment collection. A payment gateway is a user interface that enables customers to pay for goods and services via a variety of methods, channels, or both.
- Understanding Payment Gateways
- How Payment Gateways Work?
- Key Factors to Consider
- Top Payment Gateways in Nigeria
- Case Studies and Real-World Experiences
- Integration and Setup
- Security Measures
- Payment Gateway Regulations in Nigeria
- Making Your Decision
Understanding Payment Gateways
A payment gateway is what keeps the payments ecosystem working smoothly by allowing consumers and companies to make online payments. According to Statista, the Covid-19 pandemic has taken the world of eCommerce by storm, with online sales expected to reach $5.7 billion by 2022. At the same time, payment-related fraud has increased, accounting for $41 billion in losses by 2022. These data demonstrate the importance of a payment gateway in addressing the complexity of online payment processing while maintaining a seamless and secure checkout experience.
You don’t need to be a payment gateway expert if you’re an online merchant, but it’s useful to understand the foundations of how an online transaction goes from your client to your bank account.
Payment Gateways and Their Role in Online Transactions.
A payment gateway is a transaction processing technology that captures, stores, and transmits card information from the customer to the acquirer. It then shares the payment acceptance or decline notification back to the customer. In other words, the payment gateway works as the middleman between a customer and the merchant. By acting as an interface between a merchant’s website and their acquirer, an online payment gateway can simplify how merchants process card payments.
A payment gateway protects the customer’s sensitive payment data, as it relays it from the merchant to the acquirer and then the issuer using data encryption. The gateway follows several strict procedures for securing data that are defined by the PCI-DSS compliance standard, which also includes annual audits and recertifications to ensure the standard’s validity.
Importance of secure and efficient payment processing
There are tangible benefits of online payment systems for buyers and sellers. Look at some benefits your business can experience by implementing payment processing.
- 1. Increase Efficiency
Any tool that can reduce wait times will improve a business’s efficiency. Online payment systems accomplish this by providing secure and speedy channels to take, authorize, and complete electronic payments. Transaction times shrink from days or weeks to a matter of seconds.
- 2. Reduce Costs
Sending and receiving payments via paper checks can result in high processing fees for a company. Businesses may face bank fees, printing and postage costs, and secure disposal charges.
Ultimately, digital payments are a green solution that can have less or even zero environmental impact.
- 3. Improve Security
Security is a concern when handling sensitive data like customer’s credit card information and routing numbers. Some may believe that it is more secure to avoid online payment solutions because it limits access to customer data from cybercriminals.
But there are security dangers from manual processes as well. When a payment processor follows safety and security practices, it can provide a secure environment without damaging customer data.
For example, PCI-compliant payment processors must pass annual security audits by third-party verifiers. This certification signals the company is trustworthy and follows industry standards in data handling.
- 4. Improve Customer Service and Experience
Partnering with a payment processing service directly boosts the customer experience. Most customers are familiar with and prefer to use digital payments over manual ones. A company that provides multiple methods of payment – paper checks, credit cards, ACH, wire transfers, or digital wallets – will see higher customer satisfaction rates.
- 5. Reduce Fraud
Digital payments use secure and encrypted channels, making it difficult for bad actors to carry out fraudulent transactions. Customers can be confident that their electronic payments are secure when paired with features like multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- 6. Increase Compliance
Payment processors for digital payments allow a company to achieve industry standards and follow best practices. The PCI-DSS certification is the gold standard for security compliance, proving a company complies with data-handling practices and is independently checked annually.
Using digital payments often makes internal compliance an easier process as well. Electronic records may be more easily scanned for errors and cross-checked against other documents like requisitions and invoices.
- 7. Reduce Stress
Accounts payable (AP) departments tend to be understaffed and overworked. A payment processor that improves payment and spending management methods will be a helpful tool for these business professionals.
- 8. Enhance Analytics and Reporting
Payment processing platforms may have advanced metrics that give a deeper look at a company’s financial situation. Analytics allow accounts payable staffers to monitor performance and spot issues and exceptions as they arise.
Reports can also give insight into other data points that will improve efficiency and revenue:
- Customer-preferred payment methods
- Product and service selling trends
- Viable periods of increased sales
- Filtered data based on custom parameters
Granting access to aggregate data helps to avoid data silo situations where only one or two employees understand and limit decision-making ability.
- 9. System Integration
Most companies rely on multiple software systems to support their business operations, and paper processes are difficult to integrate into separate software packages. Likely, accounts payable staff will be left entering data manually multiple times, which introduces an avenue for errors to creep into data.
Having an end-to-end digital process keeps data stored electronically, making it easier to import from one system to another.
How Payment Gateways Work?
Now that you’ve understood why a payment gateway is a must-have for merchants, let’s analyze how it works throughout the payment journey. This also includes the steps taken during payment card processing – i.e., authorization, capture, and settlement.
- When the customer selects the products/services they want to purchase, they proceed to the payment page of an eCommerce website. Most payment gateways offer different options for a checkout page. emerchantpay’s payment gateway offers tailored options for your payment page that match your business needs.
- The customer enters their credit or debit card details on the payment page, including the cardholder’s name, card number, card expiration date and card verification value (CVV) number. This information is securely passed onto the payment gateway depending on the merchant’s preferred integration (hosted payment page, server-to-server integration, or client-side encryption).
- The payment gateway encrypts the card details and performs fraud checks before sending the card data to the acquirer.
- The acquirer securely sends the information to the card schemes which carry out another layer of fraud checks, and the schemes transmit the payment data to the issuer for payment authorisation.
- Authorisation – The issuer authorises the transaction once it performs the necessary fraud screening – namely, it validates the transaction information and ensures the cardholder has adequate funds for the purchase and/or that the bank account is valid. The issuer’s approved or declined payment message is transferred from the card schemes to the acquirer.
- The acquirer sends the approval or decline message back to the payment gateway which then transmits the message to the merchant. Based on the message, the merchant may either display a payment confirmation page or ask the customer to provide another payment method.
- Card capture requests – once the authorisation is completed, the merchant can “capture” the amount for the purchase from the buyer to the merchant account. The customer will not be billed until the capture has occurred, but the funds are reserved, and their card limit is reduced.
- Settlement – if the payment is approved, the acquirer collects the payment amount from the issuing bank and puts the funds ‘on hold’ into the merchant account (more on the merchant account below). When the actual settlement will happen depends on the agreement the merchant has with their payment service provider.
Both merchants and customers benefit from a payment gateway, although most of its activity happens behind the scenes of the payment process. All the steps mentioned above can happen in near real-time or take a few seconds.
Key Factors to Consider
Choosing the right payment gateway for your company is critical since it ensures robust security, safeguards sensitive information, offers a variety of payment choices, and allows for easy global transactions. Key considerations for selecting a payment gateway that meets your specific business needs are outlined below.
- Security:
Security is paramount in payment processing. Ensure that the payment gateway complies with industry-standard security features and protocols, such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard). Data security should be a top priority to protect both your business and your customers’ sensitive information. Razorpay takes security as an utmost priority with compliances to all security measures and protocols.
- Compatibility:
The most commonly used credit cards are Visa, MasterCard, and Amex. All of these card types are accepted by most payment gateways. However, if your customers usually pay you using other card types, such as a debit card or a Diners Club card, you need to make sure that your payment gateways support that card.
If you do business internationally, you need to make sure that your payment gateway can handle payments in different currencies and from different countries. It is of utmost importance to let your customers pay in their currency. You’ll also want to, check for fees involved in foreign currency transactions.
- User experience:
Simplifying user experience is crucial in the online world. A payment gateway should facilitate intuitive and hassle-free transactions to provide a smooth experience to the customer. Also, ensure mobile compatibility, as seamless payments on phones and tablets cater to modern shopping trends.
- Cost:
The most important thing you need to consider while choosing a payment gateway is the total cost that you’ll incur. The costs involved in using payment gateway comes in three types: set-up fee, monthly fee, and transaction fee.
Read Also: Which Payment Gateway is Best in Africa?
To find the most cost-effective choice for your business, both the volume and value of your transactions need to be considered. Most payment gateways have a competitive transaction fee rate of 2.9% + 30ç. This might work well for businesses when the value of their transactions is often not that high; however, if they are, the transaction fees can increase your expenses significantly. If your business deals primarily in high-value transactions, make sure you look for payment gateways that offer their services for a set monthly fee and a low transaction fee.
- Customer support:
Reliable customer support is essential, especially in case of technical issues or inquiries. Ensure that the payment gateway provider offers responsive customer support via multiple channels, such as phone, email, and live chat. Read reviews and testimonials to gauge their level of support.
Top Payment Gateways in Nigeria
To put it simply, internet payment gateways allow your consumers to make payments through your website. With so many options, we thought we’d list the best online payment gateways in Nigeria you should think about for your online business.
1. Rave by Flutterwave
Rave lets you receive payments locally and globally with no hassles and zero set-up fees. They make accepting payments online easy, safe and secure.
Unique Selling Points
- Multi-currency support: Rave’s multi-currency support allows to receive payments in multiple currencies at the flip of a switch. Rave also supports cross-currency conversions.
- Multi-tenancy possibilities: An interesting feature on Rave is the automatic white label possibilities offered absolutely free at the flip of a switch.
- Card and account payments: Rave allows you to charge cards and bank accounts directly. So you can directly debit your customers’ bank accounts.
Pricing
- Setup Fee: Free
- Local Transactions: 1.4%
- International Transactions: 3.8%
2. Paystack (now part of Stripe)
Whether you are a small or large business, Paystack offers everything you need to accept payments. It’s simple, secure and affordable.
Unique Selling Points
- Paystack is easy and free to get started: You can setup Paystack on your site or app even without a developer in minutes.
- Paystack makes sure you get paid: Payments can be completed in 2-3 easy steps. Your customers can make hassle-free payments directly on your website.
- Paystack provides tools to help you grow: Beyond payments, get reliable support and business solutions to measure and improve your growth.
Pricing
- Setup Fee: Free
- Local Transactions: 1.5% + ₦100 (The ₦100 fee is waived for transactions less than ₦2500)
- International Transactions: 3.9% + ₦100
3. VoguePay
A simple and secure way to send and receive payments globally. VoguePay’s global coverage allows consumers and businesses to safely make and receive payments in all major currencies, regardless of location.
Interestingly, VoguePay also offers safe and secure platform to accept payment in bitcoin. You can accept one-time payments, set up subscriptions, and even receive donations.
Unique Selling Points
- Multiple payment channels: Accept payment any way you want. Give your customers options.
- Developer friendly: Simple API documentation to make integration easy, even for non-developers.
- Easy Account Management: Opt for business or personal accounts based on your needs.
- Multi-currency support: Accept payment in multiple global currencies. Get paid in your default currency.
- Free integration: Easily integrate payment to your website using our plugin libraries and extensions.
Pricing
- Integration: Free (fees may apply for customization)
- Merchant Verification: ₦ 1,500 (with CAC) and ₦ 2,500 (with Govt. issued ID cards)
- Local Transactions (Naira Cards): 1.5% Transactions above ₦2,500 1.5% + ₦30
4. Remita
Remita helps you receive and make payments on your site and apps. They offer ready-to-use plugins, SDKs and APIs that make integrating a breeze.
Unique Selling Points
- Receive Payments: This offers your customers many different ways to pay you: Inline Payments, eCommerce Plugins, Mobile SDKs, and Recurring Payments
- Make Payments: Pay a single or multiple beneficiaries from bank accounts you register on Remita. Single Debit Single Credit, Single Debit Multiple Credit, Funds Transfer Plugin
- View all your Balances, On One Screen: Remita lets you see all your bank account balances, from any bank, on one screen.
- Get Paid Easier: Easily get paid by simply generating and sharing payment requests (or e-Invoices) with family, friends and customers.
- Experience True Work-Life Balance: Enjoy the convenience of switching easily from your personal to business accounts, and back again, whenever the need arises
- Easier Payroll for All Businesses: Whether you’re a 2 or 200,000 staffed organization, Remita can help manage your payroll & HR management needs.
Pricing
- Setup & Support Fees: Free
- Receiving Local Payments: 2% (Min ₦100 – Max ₦2,500)
- International Payments: 4%
5. PayU
PayU is a leading online payment service provider dedicated to creating a fast, simple and secure payment process for merchants and buyers.
Unique Selling Points
- Accept all credit cards: Expand your reach by accepting all national and international credit cards.
- Customized payment page: Customize your payment page design to ensure a consistent look and feel.
- Next day/Weekly settlement
- Added security (PCI DSS SSL and 3D secure)
- Optional fraud protection service
Pricing
- Setup & Support Fees: Free
- Payment Processing: Not specified
Case Studies and Real-World Experiences
A payment gateway’s framework differs depending on whether it is utilized in an online payment portal or in-store premises. Online payments must be hosted on the website by a third-party service provider or by the merchant via an application programming interface (API), allowing the website to communicate with the payment processing network and eventually obtain a response from the issuing bank.
A payment gateway will be used in-store either a physical card reading device or a POS terminal that links to the processing network via a secure internet connection.
The Players in the Payment Gateway Ecosystem
- Merchant or Seller
The merchant is the business or individual selling goods or services online.
To accept online payments, the merchant needs a merchant account, which is a type of bank account that allows them to receive funds from online transactions. Integrated with the payment gateway, this account allows for the secure processing of transactions. In other words, the merchant account is where all the money comes in after settlement.
To open a merchant account, you will have to research and choose a provider that aligns with your requirements.
- Customer
Customers make up the majority of participants in the payment gateway ecosystem. They make payments online through various methods such as debit or credit cards, net banking, UPI, or online wallets to purchase goods and services.
- Acquirer and Issuer Bank
Two different kinds of banks operate in the payment gateway ecosystem.
The acquirer bank, as the name suggests, acquires the payment on behalf of the merchant. This means the merchant account is housed at the acquirer bank. This is the destination for financial transactions routed through the payment gateway. In other words, this is where the money ends up.
The issuer bank, on the other hand, is where the transaction originates. This account belongs to the customer who is making the payment to pay for the product. The issuer bank represents the customer and supports the various payment methods such as credit cards, debit cards, or net banking.
- Payment Gateway
The payment gateway acts as the intermediary between the merchant’s website or app and the acquirer and issuer banks.
When the customer purchases on the merchant’s website, it is the payment gateway that allows the payment to go through. It facilitates the secure transfer of payment information and the authorization and settlement of transactions.
- Payment Processor
The payment processor is responsible for managing the technical connections between the payment gateway, the acquiring bank, and the issuer bank. It validates and routes payment transactions securely. The payment gateway and the payment processor are vital components in handling online payment transactions.
Integration and Setup
Integrating a payment gateway into a website entails many steps that are often simple. The specific method will vary based on the payment gateway you use and the platform on which your website is built, but here is a general step-by-step guide:
The first step is to select a payment gateway that aligns with your business needs. But in general, you should consider factors such as transaction fees, types of payments accepted, security measures, and compatibility with your ecommerce platform when deciding which payment gateway provider to work with.
Depending on the payment gateway, you might need to set up a merchant account—or you might not. Some payment gateway providers, such as Stripe, combine merchant account functionality in tandem with the payment gateway, offering comprehensive payment support with a seamless setup.
After setting up your account with the payment gateway, you’ll typically need to obtain API keys, which are unique identifiers used to connect an online business’s website or application to the payment gateway’s services. They are part of the system that allows secure communication between the business’s platform and the payment gateway. These keys will allow your website to interact with the gateway’s server.
This step can vary significantly depending on the payment gateway and your website’s platform. Some ecommerce platforms, such as Shopify or WooCommerce, offer plugins and extensions that make integration straightforward. Otherwise, you might need to manually add code to your website to integrate the gateway. Stripe’s APIs are very developer-friendly and easy to implement.
Before going live, test the payment gateway. Most gateways offer a “sandbox” or testing environment where you can make test purchases to ensure everything is working correctly.
Once you’ve tested the payment gateway and everything is working as expected, you can go live. At this point, customers should be able to make purchases and payments on your website.
Remember to ensure the security of your customers’ data throughout this process. Always use secure, encrypted connections and comply with Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) requirements, if you’re handling credit card information.
As you can see, the payment gateway market has a lot to offer you. However, if none of them seem to meet your company’s requirements, there is always the option of developing your own payment gateway for an eCommerce website.
Creating a custom payment service is not an easy undertaking. You must first complete the following steps:
- Registration. You need to be registered as a payment gateway provider in your bank.
- Contracting with banks. In order to have payment processors, you need to deal with different banks. They offer you diverse fees for transactions, international transfers.
- API development. You definitely need API for your gateway. At this stage, you also have to deal with piles of documentation.
- PCI DSS certification. To meet the requirements of PCI you should install reliable mechanisms against fraud on your website.
- Add more payment methods. Integrate methods like PayPal, Bitcoin, or mobile wallets (e.g. Apple Pay), with the help of their APIs.
- Management tools development. You will need at least an admin panel to control transaction operations more easily.
Custom gateway will consume a lot of money and no less effort. Don’t forget about the time needed to launch a ready-to-use payment system and implement it into your business.
On the other hand, the advantages will make you think once again. You won’t have to pay high transaction fees offered by ready payment solutions. Besides, your payment gateway means it is developed in full accordance with your business’s needs. Invest now and enjoy revenues in the course of time.
Security Measures
Many businesses rely on payment processing firms to manage their internet payments. However, relying solely on a third party might cause organisations to undervalue their payment gateway security risks and requirements, leaving them vulnerable to data breaches and cybercrime. This problem is exacerbated when businesses undergo changes like as expanding operations or transitioning to a subscription billing model.
According to the PWC Global Economic Crime and Fraud Survey 2022, 52% of organisations with global annual revenues above $10 billion experienced fraud in the previous 24 months, with 18% losing more than $50 million in their most disruptive episode. 38% of smaller organisations earning less than $100 million per year encountered fraud; 22% of those impacted faced a total effect of more than $1 million.
Payment gateway security is critical for safeguarding your customers’ personal information and securing your business. Security breaches, fraud, and compliance violations are all costly blunders that not only jeopardise your hard-earned cash but also jeopardise the reputation of your company.
Breach or theft of cardholder data can result in fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global revenue, whichever is greater, under the European Union General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Furthermore, payment providers have the authority to sanction organisations that violate the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) $5,000-$100,000 per month for noncompliance.
As more customers turn to e-commerce for their purchasing requirements, businesses must be prepared to deliver a secure shopping experience.
Continuous learning is foundational to creating a culture of data security, so it’s critical that your team remain updated on the latest safety strategies and regularly evaluate whether it’s time for an upgrade. Below you’ll find five payment gateway security features that are necessary in today’s business climate.
- 1. PCI DSS Compliance
Any company that processes credit or debit card purchases must comply with the international rules and regulations stated in the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). The main role of the PCI DSS is to provide businesses with a standardized approach to rigorous, secure transaction processes while retaining a smooth customer experience.
Maintaining PCI compliance is essential to avoiding penalties and improves your reputation with payment brands, builds customer trust, and bolsters your systems to prevent data breaches and credit card fraud. The PCI DSS has 12 key requirements, further broken down into 78 base requirements and 400 test procedures. The 12 key requirements are outlined in the image below:
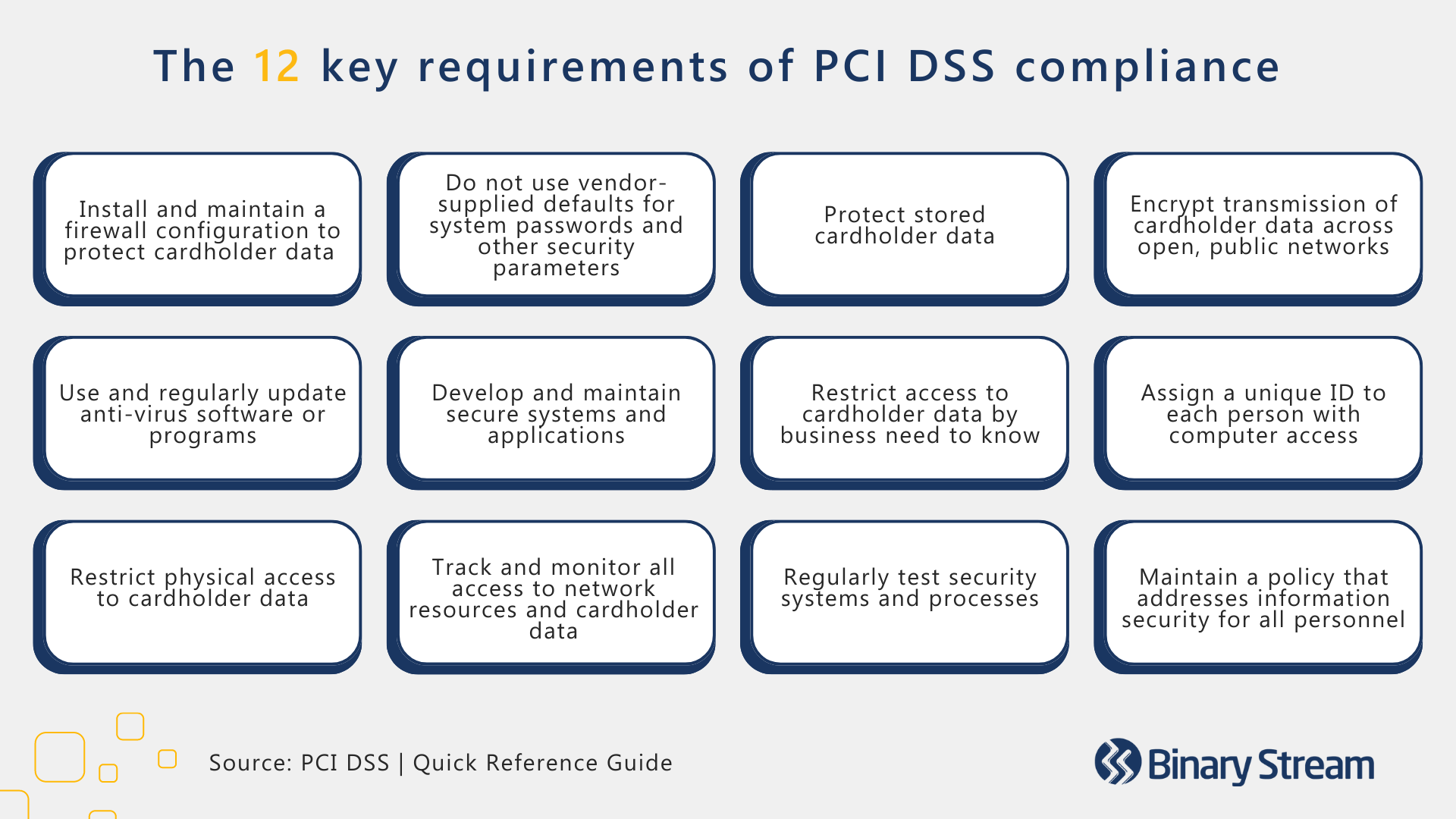
Companies must adhere to different compliance levels based on their size. The PCI classifies businesses on a four-level scale by the number of transactions they process per year:
- Level 1: >6 million card transactions annually.
- Level 2: 1–6 million card transactions annually.
- Level 3: 20,000–1 million card transactions annually.
- Level 4: <20,000 card transactions annually.
All legitimate processing providers are required to offer PCI-compliant services; however, it’s still worth investigating the PCI DSS as your business will be on the line for any non-compliance. When determining which payment processor to invest in, make sure it can manage credit card processing, transaction history, and credit card data management while complying with the PCI DSS.
- 2. SSL and TLS protocols
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols encrypt the online connection between the browser and the server, creating end-to-end protection for sensitive information. These security measures ensure the secure transmission of customer data collected by a payment gateway.
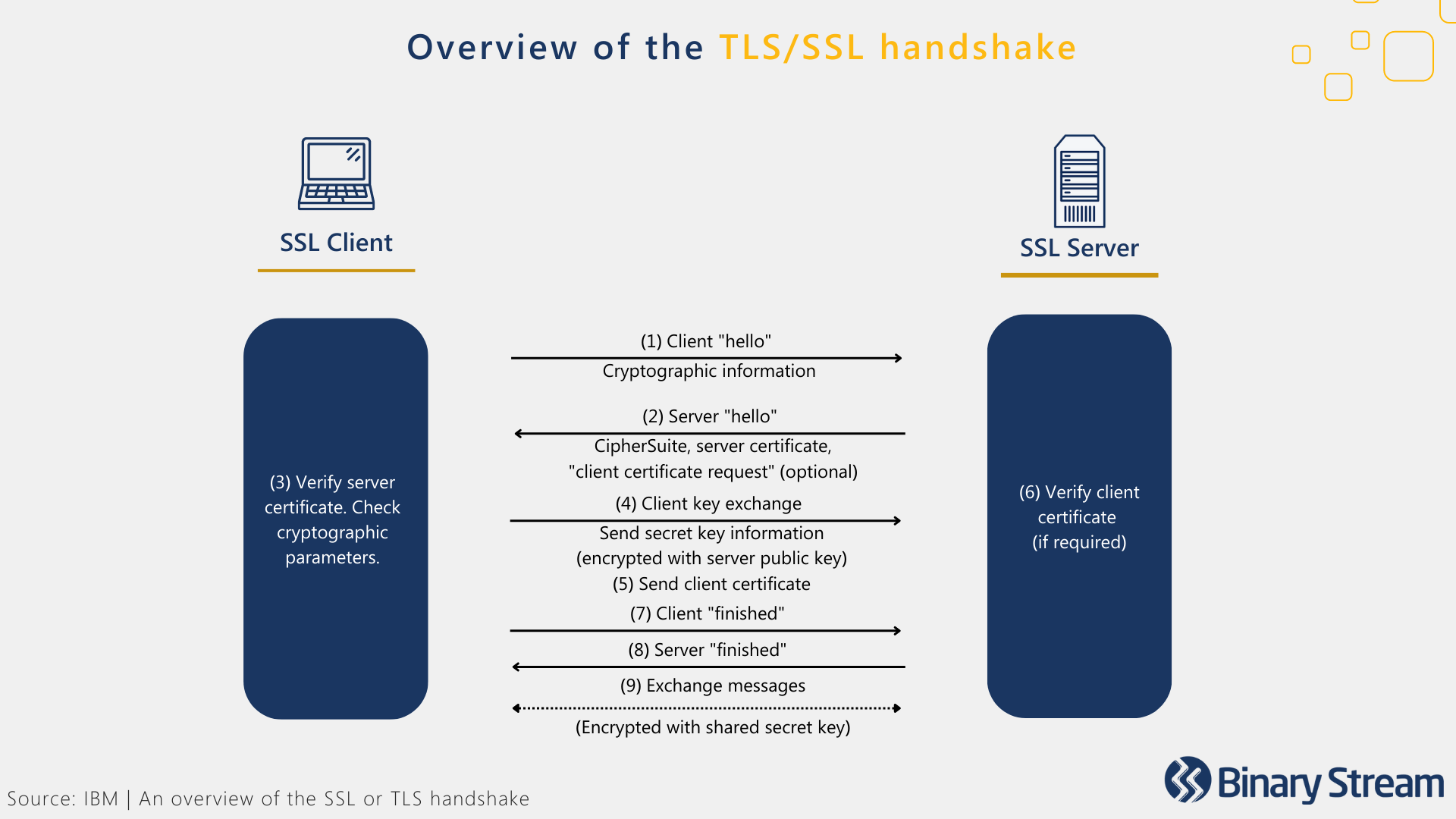
Here’s an overview of how the encryption process, nicknamed the “TLS/SSL handshake,” works:
- Each TLS/SSL certificate involves a public key and a private key.
- When a customer visits the website, the customer’s server and the web browser communicate to determine if there’s a secure TLS/SSL encrypted connection.
- When the web browser directs to the website, the website server shares its TLS/SSL certificate and public key with the customer to establish a secure connection, generating a unique session key.
- The browser confirms that it recognizes the issuer of the TLS/SSL certificate (Certificate Authority) and that the certificate is not expired, revoked, or untrustworthy.
- The browser sends over the session key, and the server uses its private key to decrypt the session key.
- The server then sends back an encrypted acknowledgment using the session key to start the encrypted session.
- The server and browser can now encrypt all transmitted data with the session key, creating a secure session that fortifies all shared data’s privacy, integrity, and security.
If you’ve ever visited a website where the URL begins with HTTPS or has a padlock symbol next to it, then you’ve encountered TLS/SSL encryption. These hallmarks signify that the website is TLS/SSL certified and that your customers can trust your company with their payment information.
- 3. 3D Secure
3D Secure (3-domain structure) or payer authentication, is a security feature that addresses issues of fraud in online debit or credit card transactions. Customers are required to complete an extra step of verification with their card issuer at checkout, engaging all three domains of payer authentication:
- The merchant/acquirer domain
- The issuer domain
- The interoperability domain
The most recent iteration, 3D Secure 2, allows for different methods of verification other than a password, including:
- 2FA (2 factor authentication): Using two different authentication factors, such as a username and password combination and a phone.
- Biometric identification: fingerprint, face, or voice recognition.
- Risk-based authentication: a flexible approach to authentication, requiring different protocols based on the customer’s risk profile.
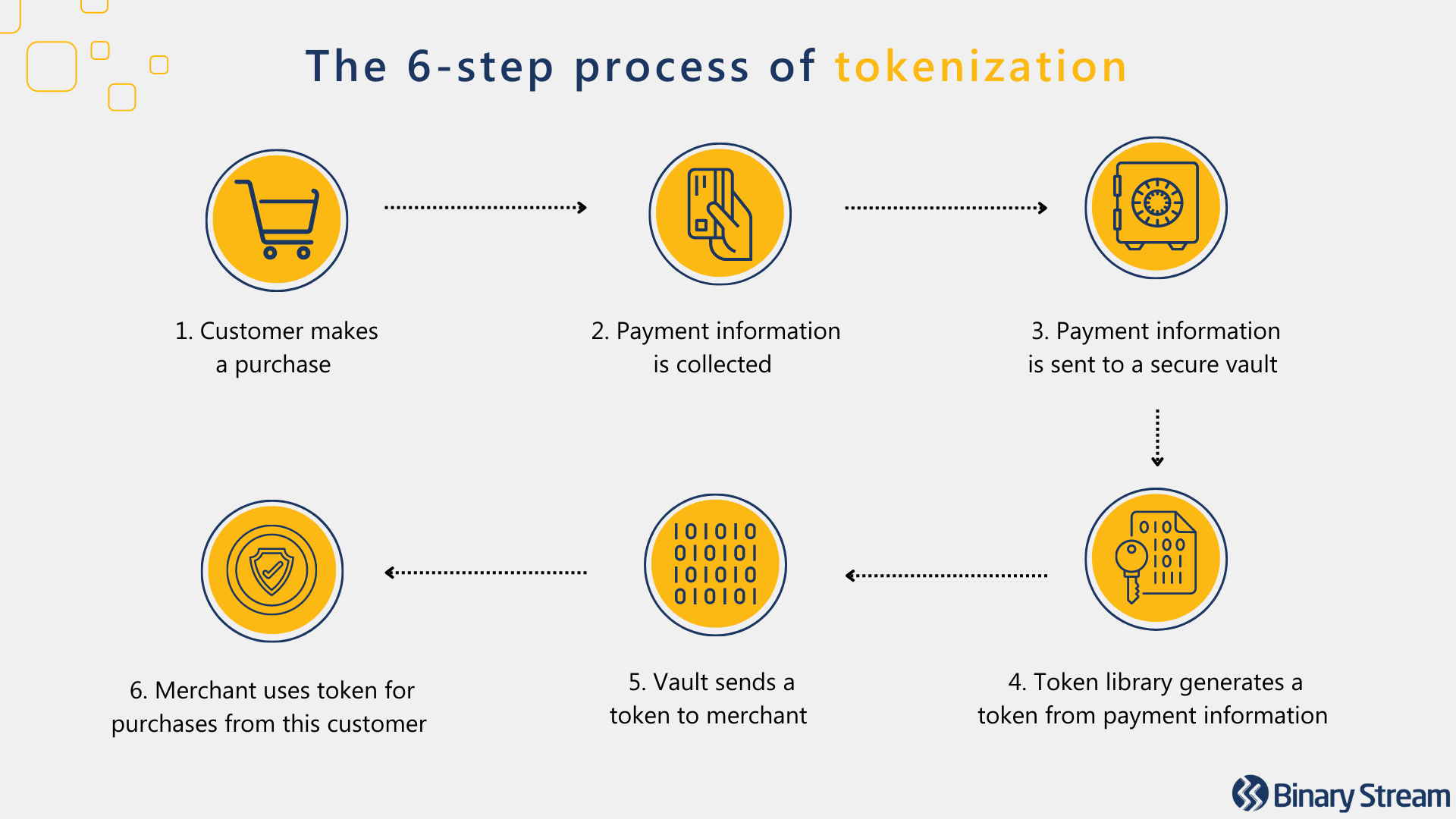
- 4. Tokenization
Tokenization secures customer payment details by replacing sensitive data with a string of randomly generated numbers, referred to as a ‘token.’ The PCI DSS promotes the adoption of payment tokenization with good reason.
Tokens provide one-to-one replacements for primary account numbers kept outside the merchant’s server. The merchant does not need to be responsible for storing sensitive information, protecting the merchant and customer against fraudulent activity.
This extra layer of protection renders confidential information meaningless and useless in a breach. If a hacker were to gain access to the tokens, their efforts would be wasted because they would have no way to decrypt them.
- 5. Address Verification Service
The address verification service (AVS) is another commonly used method to prevent credit card fraud. After a customer enters their billing address, AVS will check if it matches the one on file with the credit card provider. If it’s a match, then the transaction will be approved.
AVS can be an effective protocol for minimizing chargebacks. Verifying details about the cardholder provided during the purchasing process can help flag suspicious transactions and protect the company before fraud occurs.
Payment Gateway Regulations in Nigeria
The most common forms of fintech enterprises in Nigeria include mobile payments, payment processing, mobile lending, and personal finance.
The payments and remittance subsector has become a source of investment interest in Nigeria. In 2006, the Central Bank of Nigeria (“CBN”) released the Payments Systems Vision 2020 (“PSV 2020”) to provide a roadmap for reforming the Nigerian payments system. It focused on promoting the adoption of electronic payments and improving the resilience of the Nigerian financial system.
Given the ensuing successes, the CBN in 2022 published the Nigeria Payments System Vision 2025 (“PSV 2025”), which focused on driving digital innovation and payments, particularly in areas such as big data, contactless payments (“CP”) and open banking. Over the course of 2022, the CBN took a number of steps to achieve the objectives of the PSV 2025.
In October 2022, the CBN issued an Exposure Draft of the Guidelines for Contactless Payments in Nigeria (the “Draft Guidelines”) which, when approved, will provide a framework for CP services in Nigeria. The Draft Guidelines identify the key stakeholders in CP transactions, which include acquirers, issuers, payment and card schemes, switching companies, merchants, and customers. The Draft Guidelines also set out the minimum standards that all stakeholders must comply with while providing CP transactions. With CP transactions becoming more popular globally and gaining ground in Nigeria, it is hoped that the Draft Guidelines will become operational in the coming months.
In addition, the CBN also issued the Draft Operational Guidelines for Open Banking in Nigeria 2022 with the aim of establishing a framework for standardizing open banking practices in the Nigerian financial industry and simplifying the process of information sharing between participants. The open banking guidelines have now been approved and came into effect in 2023.
In 2022, the CBN announced plans to set up a national domestic card scheme, the first central bank-led national card scheme in Africa. A national domestic card scheme is a card scheme that is fully owned by the government of a country. AfriGo, as it is called, has been set up with the aim of improving the level of usage of electronic platforms in Nigeria and strengthening the national payments system.
Furthermore, as part of the CBN’s drive to improve the rate of financial inclusion, in 2022, the CBN gave its final approval for two payment service banks (“PSBs”) to commence operations. The two PSBs are backed by two of the biggest telecommunications companies. Given the large customer base of these Telcos, it is hoped that they will be able to reach previously unbanked customers, thereby improving the rate of financial inclusion in Nigeria.
One of the most significant policies of the CBN in 2022 was the introduction of strict withdrawal limits in furtherance of its cashless policy following the redesign of some denominations of Naira notes. To promote the use of electronic payment channels, the CBN set a weekly over-the-counter cash withdrawal limit of NGN500,000 for individuals and NGN5 million for corporates, with withdrawals above these limits attracting a processing fee of 5% and 10% for individuals and corporates, respectively.
In relation to withdrawals via automated teller machines (“ATMs”), the CBN set a maximum withdrawal limit of NGN100,000 per week, subject to a daily limit of NGN20,000. The daily maximum withdrawal limit for ATMs was also to apply to point of sale (“POS”) terminals. ATMs were to only be loaded with lower denominations from NGN200.
Making Your Decision
A payment gateway is required if you wish to accept credit cards, digital wallets such as Apple Pay and Google Pay, and local payment methods such as Bizum, to mention a few. But where do you begin when it comes to selecting the finest payment gateway for your e-commerce business?
It is critical to examine alternatives and select a payment gateway that meets your specific business requirements. Consider where your consumers are situated, what payment methods they prefer, your long-term growth ambitions, and other aspects.
Here are some general things to consider when choosing a payment gateway:
- Third Party Gateway vs Platform Native Gateway. If you decide to use a third party payment gateway, customers will be directed to an external payment gateway to submit all of the payment information away from your website so they can check out and complete the transaction. The customer will then be redirected back to your site after the transaction has been completed on the external payment gateway site. Payment gateways that are integral software to your ecommerce platform have customers submit payment information and process the transaction completely on your website.
- Bundled Payment Gateway and Merchant Account. Many payment gateways offer a merchant account that is bundled with a payment gateway service. You use the payment gateway’s merchant account to hold the funds until they are permanently transferred to your business’s bank account. Many smaller businesses choose this option because it is often easier to set up and has lower monthly fees, but in some instances, additional per-transaction fees could be applied depending on the gateway you choose. It is important to note that if your business has its own merchant account and would like to add a payment gateway to its site, you should ensure that the payment gateway you select is compatible with your current merchant account.
- Cost. Cost can be broken down into two separate components: monthly fees, which are recurring fees regardless of the order volume of your site, and per-transaction fees, which are based on the number of transactions that occur on your site and are either fixed or variable. Additionally, some payment gateways offer a volume discount if your business website conducts a high volume of sales through the payment gateway.
- Reputation. This criterion is a vital, though often intangible, element to a payment gateway, because knowledgeable customers will make purchases from your site only if they recognize and trust the payment gateway you offer. Most major payment gateways are safe and reliable, but the customer’s perception of the reputation of the payment gateway is crucial to your site’s success.
- Payment Methods Accepted. Payment method simply refers to which credit card companies the payment gateway accepts (Visa, MasterCard, etc.) and whether the payment gateway is able to directly accept bank account payments. Most major payment gateways accept all major credit card companies, but whether your desired payment gateway service will accept certain foreign credit card companies and currencies will vary. Some payment gateways have their own customer accounts (such as PayPal and Dwolla), in which customers have an account directly with the payment gateway to pay for products on your site. Businesses that are exporting or are planning to export should pay close attention to this criterion and should once more consider that credit card companies will always side with the cardholder in any overseas credit dispute situation.
- Payment Gateway Supported by Your ecommerce Platform. Once you have made a choice on which ecommerce platform to use for your website, you must next ensure that the ecommerce platform will support your preferred payment gateway. Many of the major payment gateways are accepted by most major ecommerce platforms, but if you do not ensure that they are compatible, then you will soon discover that receiving payments into your business bank account from transactions on your website will be much more difficult. To check compatibility of a payment gateway with your ecommerce platform, simply visit your ecommerce platform’s vendor website, and check over the list of plugins and extensions for your preferred payment gateway.
A growing number of businesses are offering more than one payment gateway on their site. Most commonly, a site will have a non-hosted payment gateway option to directly enter payment information on the site in addition to a hosted gateway option (such as PayPal), which will direct customers off the site to enter payment information. Although offering two payment gateways is more expensive, it allows customers to select the option they are more comfortable with. Depending on your customer base, this offering could be a smart option for your business.
Conclusion
When choosing a payment gateway, look for those that support a variety of payment methods, including credit cards, Apple Pay, Google Pay PayPal, Bizum, Click to Pay, and other popular payment options. This way you can accommodate the payment preferences of your customers.
Security should be a top priority when choosing a payment gateway. Look for payment gateways that offer strong security measures, such as SSL encryption and PCI compliance, to protect your customers’ payment information and prevent fraud.
To compare fees and costs between payment gateways, look for clear and transparent pricing information on their websites. Consider factors such as transaction fees, monthly fees, and other costs. It’s also a good idea to calculate the total cost of each payment gateway over time, including any hidden or unexpected fees, to make sure you’re getting the best deal.


