Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a revolutionary force in the constantly evolving finance sector, redefining the conventional role of financial analysis. AI has established itself as a key component of the financial industry thanks to its capacity to handle enormous datasets, implement predictive analytics, and enhance decision-making procedures.
But like with every technical development, there are obstacles to overcome, such worries about cybersecurity and ethics. As we look ahead, we’ll also look at potential trends, with a particular emphasis on how machine learning will continue to be integrated and how human expertise and AI skills will work together more and more.
This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of AI’s current and future implications in financial analysis, ultimately encouraging financial professionals to embrace these advancements for future success.
The process of assessing a company’s financial sustainability, performance, and health is known as financial analysis. Examining its financial accounts, metrics, and other pertinent data is how it is accomplished. The aim is to obtain significant insights that facilitate decision-making, be it for strategic planning, internal management, or external investment considerations.
Financial analysis also includes evaluating a company’s profitability, liquidity, solvency, and general financial stability by assessing its financial data.
Critical Aspects of Financial Analysis
- Data Examination: This involves scrutinizing financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, to understand a company’s financial position.
- Ratio Analysis: Calculating and interpreting financial ratios (e.g., liquidity ratios, profitability ratios, solvency ratios) to assess various aspects of a company’s performance.
- Trend Analysis: Evaluating historical financial data to identify patterns, trends, and changes over time, providing insights into the company’s performance trajectory.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparative analysis compares a company’s financial performance to that of its industry, competitors, or historical performance.
- Forecasting: Using historical data and trends to predict future financial performance, helping with strategic planning.
- Qualitative Assessment: Considering non-financial factors such as management expertise, industry trends, and market conditions that may impact financial performance.
Benefits of AI in Finance Analysis
Here are six benefits of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in finance, along with explanations for each:
Enhanced Efficiency
AI automates routine and time-consuming tasks such as data entry, reconciliation, and report generation. This increases operational efficiency as AI systems can process large volumes of data at high speeds, freeing human resources to focus on more strategic and value-added tasks.
Improved Decision-Making
AI provides data-driven insights and predictive analytics, enabling more informed decision-making in finance. Algorithms analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, and offer valuable information to financial professionals, assisting them in making optimal choices related to investments, risk management, and strategic planning.
Fraud Detection and Security
AI-powered tools excel at detecting anomalies and patterns associated with fraudulent activities. By continuously monitoring transactions and identifying suspicious behavior, AI contributes to strengthened security measures, reducing instances of fraud and safeguarding sensitive financial information.
Personalized Financial Advice
AI analyzes user data, financial goals, and market conditions to provide personalized investment advice. This tailoring of financial guidance helps individuals optimize their investment strategies based on their unique preferences, risk tolerance, and financial objectives, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Automation of Back-Office Processes
AI automates routine back-office tasks, including data entry, reconciliation, and compliance reporting. This increases operational efficiency by reducing manual workload and minimizing the risk of errors associated with repetitive tasks, allowing financial professionals to focus on higher-value and strategic activities.
Market Analysis and Trend Prediction
AI analyzes market trends, news, and social media sentiment to predict market movements. By providing real-time insights and quick reactions to changing market conditions, AI assists financial professionals in making more informed decisions and devising effective investment strategies.
How Is AI Used in Finance?
The banking sector makes extensive use of artificial intelligence (AI), which is transforming conventional procedures and opening up new avenues for creative problem-solving. This is a summary of AI’s applications in finance.
1. Algorithmic Trading
Artificial Intelligence is prominent in algorithmic trading in finance. AI algorithms are critical in analyzing market data, identifying intricate patterns, and executing trades at speeds and frequencies that exceed human traders’ capabilities.
AI improves trade execution by processing real-time market data, ensuring precision and speed. Furthermore, the efficiency of trading operations is significantly increased as algorithms adeptly handle large datasets, outperforming traditional methods.
Furthermore, AI’s ability to respond quickly to market changes enables traders to capitalize on real-time opportunities, ushering in a paradigm shift in the agility of financial decision-making.
Renaissance Technologies, a hedge fund known for leveraging AI and quantitative algorithms in high-frequency trading, is a striking example of AI’s transformative impact in algorithmic trading. The hedge fund has achieved exceptional returns and redefined financial decision-making through the strategic integration of AI.
2. Risk Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is also significant in risk management. AI critically assesses and forecasts risks by analyzing large datasets, market conditions, and historical trends. This critical function provides an array of advantages. AI models that can thoroughly analyze data contribute to improved risk assessment, resulting in more accurate evaluations.
Furthermore, the real-time insights of AI systems allow financial institutions to proactively implement risk management strategies, ensuring a quick response to evolving scenarios. The impact extends to better decision-making in critical areas like credit, market, and operational risks, where AI integration augments the ability to make informed and strategic choices.
JPMorgan’s use of AI for credit scoring is a notable example of AI’s ability in risk management. The technology dramatically improves credit assessments, making risk evaluations more accurate and demonstrating AI’s transformative role in financial risk management.
3. Fraud Detection and Security
AI is critical to fraud detection and security. Artificial intelligence-powered tools are used to analyze transaction patterns, identify anomalies, and detect potentially fraudulent activities. The advantages of incorporating AI into fraud detection and security are numerous. For starters, it improves security by actively detecting and preventing fraudulent transactions. This proactive approach contributes significantly to the cybersecurity framework, ensuring a strong defense against unauthorized access and activities.
Second, the use of AI-powered automated detection systems allows for the rapid identification of suspicious activities, reducing the incidence of fraud. The effectiveness and speed with which AI recognizes patterns and anomalies are critical in mitigating the risks associated with fraudulent financial activities.
Finally, AI helps to protect sensitive financial information. AI assists in creating a secure environment for handling and safeguarding confidential financial data by leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning.
Mastercard, for example, incorporates AI into its decision intelligence platform, which analyzes transaction patterns to identify potential instances of fraud. This implementation prevents unauthorized transactions and ensures secure financial transactions for cardholders.
4. Customer Service and Chatbots
An essential use of AI in finance is customer service and chatbots. AI-powered chatbots play a multifaceted role, as they are designed to provide customer support, respond quickly to queries, and assist with routine tasks. AI integration, customer service and chatbots offer numerous benefits to the financial industry. For starters, AI-powered chatbots increase customer engagement by providing instant responses, thereby improving overall satisfaction and interaction.
Read Also: Measuring The Impact of Video Marketing Through Data Analytics
Furthermore, these chatbots are available 24 hours a day, seven days a week, ensuring consistent availability and support for customers regardless of the time of day. This around-the-clock service enhances accessibility and responsiveness, fostering a positive customer experience.
In addition, AI is critical to the efficient handling of routine inquiries. AI allows human agents to devote their time and expertise to more complex and intricate issues by automating responses to frequently asked questions and routine tasks, improving the overall efficiency of customer service operations.
One example is Bank of America’s virtual assistant, Erica, which uses AI to provide personalized financial advice, answer customer questions, and assist with routine banking tasks. Erica’s integration exemplifies the practical application of AI in improving the overall customer experience in the finance industry.
5. Personalized Financial Advice
AI plays a significant role in the financial industry, particularly in personalized financial advice. The primary function of AI in this context involves the analysis of user data, financial goals, and market conditions to generate tailored investment advice.
This personalized approach offers several advantages. Firstly, AI can provide tailored financial guidance by considering individual financial goals and risk tolerance, ensuring that the advice aligns with the unique needs of each user.
Additionally, the use of AI in generating personalized recommendations contributes to optimizing investment strategies for individuals, enhancing the likelihood of achieving their financial objectives. Beyond the financial aspect, incorporating AI into providing customized advice contributes to an overall improved customer experience, as users receive guidance specifically designed to meet their financial needs and aspirations.
A notable example of this application is Wealthfront, a robo-advisor that utilizes AI algorithms to analyze user preferences, financial goals, and market conditions. Through this analysis, Wealthfront can offer personalized investment advice and create customized portfolios for their clients, exemplifying the practical implementation of AI in delivering tailored financial solutions.
6. Automation of Back-Office Processes
AI also automates back-office processes, such as data entry, reconciliation, and report generation, which helps streamline routine and time-consuming tasks. The role of AI in this context is critical, with its automation capabilities bringing numerous advantages.
Implementing AI-driven automation increases operational efficiency by significantly reducing the manual workload associated with repetitive tasks. As a result, financial institutions can handle their operations more quickly and accurately. AI systems also contribute to significantly reducing errors, as these systems are designed to reduce the risk of human errors in routine back-office operations.
Aside from reducing errors, implementing automation in back-office processes allows financial professionals to focus on higher-value and strategic activities. AI-driven automation liberates time and resources rather than burdening them. This allows financial professionals to focus on tasks that require analytical thinking and strategic decision-making.
UiPath, a platform that uses robotic process automation (RPA) to automate various back-office processes in finance, such as data entry, reconciliation, and compliance reporting, is a tangible example of this application. UiPath shows how AI can automate back-office tasks to improve financial operations.
7. Market Analysis and Trend Prediction
AI is important in the financial sector, particularly in market analysis and trend prediction. The core function of AI is to forecast and predict market movements by analyzing market trends, news, and social media sentiment.
The use of AI in market analysis has several advantages. For starters, it enables better-informed decision-making by providing valuable insights into current market trends, allowing financial professionals to make strategic decisions based on a thorough understanding of the market landscape.
Furthermore, AI’s rapid analysis capabilities enable quick reactions to changing market conditions, ensuring financial entities can quickly adapt to dynamic environments. Also, AI’s use of predictive analytics aids in developing improved investment strategies, increasing the effectiveness of financial decision-making processes.
Kensho, an analytics and knowledge platform that uses AI to analyze financial markets, is a tangible example of the application of AI. Kensho analyzes massive amounts of data, including news and events, to provide real-time insights and forecast market trends. This demonstrates the practical application of AI in improving market analysis and prediction capabilities in the financial industry.
8. Regulatory Compliance
AI helps financial institutions comply with regulations. Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a critical role in this domain by automating compliance processes and continuously monitoring transactions to detect and address suspicious activity. The benefits of incorporating AI into regulatory compliance are numerous.
Artificial intelligence (AI) ensures enhanced compliance with complex regulatory frameworks. This gives financial institutions a systematic and efficient approach to navigating and adhering to intricate legal requirements.
Furthermore, because AI systems are designed to detect and correct potential breaches in real-time, their use significantly reduces the risk of regulatory penalties associated with noncompliance. This protects institutions from financial penalties and reinforces their commitment to regulatory compliance.
Furthermore, AI-enabled automated monitoring ensures that financial transactions adhere to legal standards, contributing to financial operations’ overall integrity and transparency.
Nasdaq SMARTS is a concrete example of the use of AI in regulatory compliance. This solution employs artificial intelligence (AI) for market surveillance and compliance, assisting financial institutions in detecting and preventing market abuse while adhering to strict regulatory standards.
9. Quantitative Analysis and Portfolio Management
AI also plays a pivotal role in quantitative analysis and portfolio management. The core function of AI in this context involves the analysis of vast amounts of financial data to optimize investment portfolios and execute quantitative strategies. Incorporating AI in quantitative analysis and portfolio management brings several benefits.
Firstly, AI improves portfolio performance by leveraging data-driven insights to optimize investment portfolios. This data-centric approach enhances the precision and effectiveness of investment strategies, leading to better overall performance.
Additionally, AI aids in better risk management within portfolios, as AI models are adept at assessing and managing risks more effectively than traditional methods. This, in turn, enhances the overall risk management framework for investment portfolios. Furthermore, the efficiency of AI in processing large datasets quickly enables more efficient and data-driven investment decision-making.
As an illustrative example, BlackRock’s Aladdin is a widely adopted platform that harnesses AI for portfolio management. Aladdin analyzes financial data, market trends, and risk factors to optimize investment portfolios, mainly catering to institutional investors.
5 Unique Ways to Use AI in Data Analytics
In a separate article, we explore whether AI will replace programming. In it, we conclude that the most likely outcome is that AI will instead supplement those working in data analytics and programming. Here are some of the ways to use AI in data analysis:
1. Generating code & debugging errors
First up, you’ll most likely be using AI for generating code or debugging errors in data analysis. This is particularly helpful for complex tasks, such as visualizing large datasets and building machine-learning models.
Some common AI coding assistants you can use include DataCamp Workspace AI, Anaconda Assistant, Jupyter AI, and GitHub Copilot.
For generating code, you’ll be able to use them to create code blocks for analysis. For example, you can prompt the Jupyter AI from within your programming environments in Python as long as it runs the IPython kernel.
Additionally, if you’ve written some more complex code by yourself and have some trouble explaining it in text, you can ask the AI to comment on your code for you. In this manner, you can quickly save time on the tedious documentation process.
You can also get the AI to provide you with code completions, where you can begin typing a function and have the AI complete the rest of the code based on the information you included in your comment.
These tools are also able to debug errors you encounter, so the process of searching for a solution is shortened greatly.
If you’re an Excel user, Microsoft 365 Copilot can also help with creating formulas and macros.
2. Explaining analysis & insights
In data analytics, explaining insights and diving deeper into the data is sometimes necessary to extract true business insight. That’s where an AI can help. Using AI tools for data analysis like Tableau GPT, you can quickly explain a specific data point on a chart is behaving a certain way and provide deeper insights into it.
For example, you can ask straightforward questions such as:
- “Why did the sales decrease in March?”
- “What could be the cause of the spike in users?”
- “Which is our best revenue quarter for the year?”
The AI chatbot will then scan through your datasets to identify trends and correlations that could provide you with answers to your questions.
This function could also be used for other purposes, such as exploratory data analysis when encountering a new dataset or database in your data analytics project.
3. Creating Synthetic Data
Another useful application of AI in the field of analytics is the production of synthetic data. In fact, according to a Gartner report, it is predicted that future AI models will be mostly trained by synthetic data by 2030.
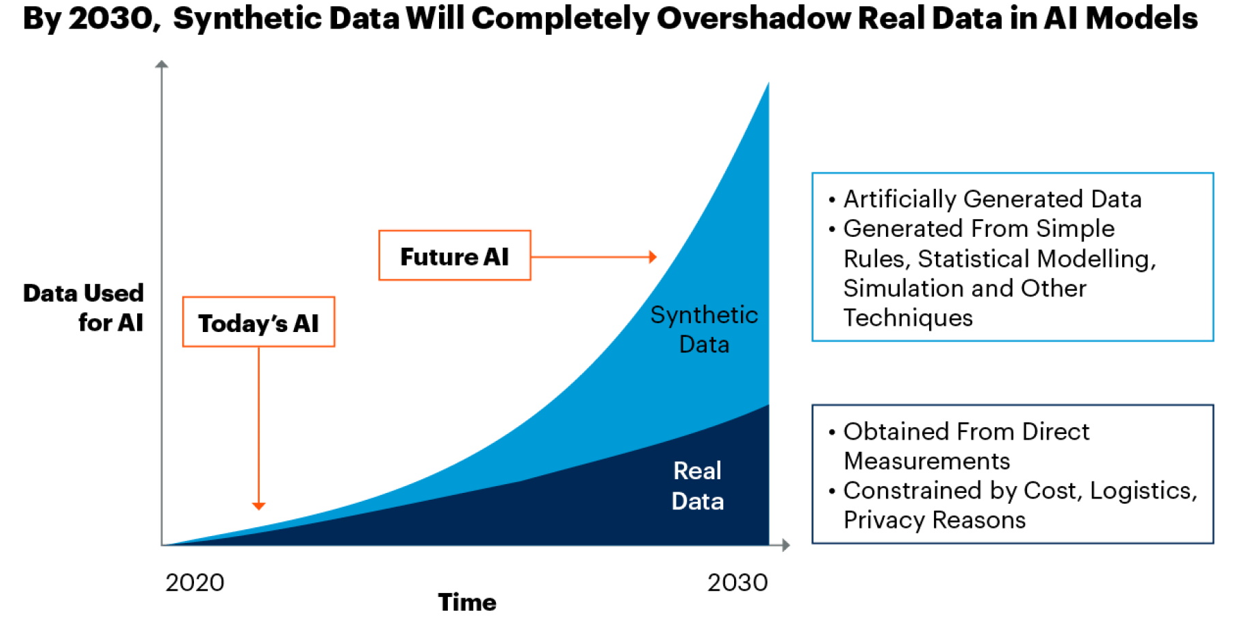
This can be especially useful for machine learning engineers and data scientists. For example, training datasets can be generated and fed into machine-learning models. This can be done through either free tools like ChatGPT or paid tools like Mostly AI or Gretel AI.
This makes it easier to test out different models and see how they perform with the generated data. This is especially useful if you’re in need of some training datasets that are harder to obtain, like various forms of media, including images and videos.
Another way that AI can help with data analysis is through automated data imputation. Automated imputation can help fill out datasets with missing values or outliers more accurately and quickly.
4. Creating Dashboards & Reports
Next, AI can be used to create interactive dashboards and reports. For example, you can use an AI-driven tool like Tableau GPT to quickly aggregate data from multiple sources into a user-friendly dashboard or report.
You don’t even need to have any prior experience in the field of data visualization. All you need to do is select the data you’d like to include in the visualization, and the AI will automatically format it into a user-friendly chart or graph.
In addition, another unique way to use AI to assist with creating beautiful charts is to use the Midjourney AI to generate some eye-catching ideas for dashboards relevant to your analysis.


